FW 3.XX (Auto) Provisioning
Introduction
The beroNet Gateways and Cards can receive their configuration via tftp or http. This method can be used to automatically provision the devices. The basic concept is, that the same configuration files that are provided via the backup function, can be used to provision the device. This gives the user the possibility to configure the device in the way he wants via the GUI and then simply download the backup of this configuration and use it to provision multiple devices at once and automatic.
The provisioning method has evolved throughout the firmware releases:
- Firmware 1 and 2 had http/tftp provisioning which needed to be triggered by using the API
- Firmware Version 3 introduced DHCP auto-provisioning
- Firmware Version 16 introduced a new API, XML - style of backups and single file provisioning
This document provides a step by step guide on how to provision the beroNet Gateways and Cards.
Prerequirements
In order to provision beroNet devices you will need control over at least a web- or tftp-server. This server provides the configuration files either as plain files or generated via a script. Starting from firmware version 3 you will need control over a DHCP server, only if you want to use auto-provisioning via DHCP.
Provisioning with Firmware 3.XX
The backup and provisioning uses the backup file package which can be downloaded in the WebGUI of the device.
The first steps to setup a provisioning environment are:
- setup a http/ tftp server
- configure a gateway / card in the way you want it to behave
- download the beroNetGW-xxx.tar.gz backup package file
- unpack the beroNetGW-xxx.tar.gz file on the webserver
- test if you can download the file with a browser
The beroNetGW-xxx.tar.gz file name contains several information. The structure of the name is:
beroNetGW-$SERIALNUMBER$-backup.tar.gz
one example is:
beroNetGW-3-04-0000016254-backup.tar.gz
After unpacking this .tar.gz the following files will be present:
file | description | mandatory? |
|---|---|---|
| hardware.conf | hardware and module related settings, like TE/NT and Synchronization Port for ISDN Ports | always mandatory |
| isgw.analog | contains the port groups and the group configuration for analog ports (FXS/FXO) | only if analog module present, otherwise emtpy |
| isgw.cas | contains CAS groups and their configurations (T1 module) | only if T1 module is present and set into CAS mode |
| isgw.causes | contains the ISDN causes to SIP response code map | always mandatory |
| isgw.conf | contains general configuration settings like logging and pcm bridging | always mandatory |
| isgw.cpt | call progress table for mapping SIP STATUS responses to ISDN STATUS Messages | mandatory but can be empty most times |
| isgw.dialplan | Dialplan which connects the technologies and contains number rewriting rules | always mandatory |
| isgw.gsm | contains GSM groups and their settings (GSM Module) | only if gsm module present, otherwise empty |
| isgw.isdn | contains the ISDN BRI and PRI groups and their settings | only if ISDN module present, otherwise empty |
| isgw.sip | contains the SIP Accounts and their configurations | only if SIP is used, general part should be provided always |
| isgw.tones | contains the tones definition | optional if you want to change the tones settings |
| misc.conf | contains several system related settings like network, snmp and cloud | always mandatory |
| network.acl | contains the firewall rules | always mandatory |
You will also need to add a provisioning configuration file, which tells the device if it should download these files or not. This file has the name "conf-update.conf" and contains only one line:
CONF_DOWNLOAD=yes
Only when you create this file, the device will attempt to download the other configuration files.
When the setup is ready and the files from the backup can be downloaded via a browser the next step is to inform a gateway about the location of these files. The gateway can receive information about the location via several ways:
- manual configuration via the GUI
- automatic configuration via the API
- automatic configuration via DHCP
Provisioning URL
In any case the location of the configuration files is an URL including the server and the directory where the files reside. The beroNet devices support special variables that can be used in the URL:
- {mac} - is replaced by the Ethernet MAC-Address of the device that requests the URL
- {serial} - is replaced by the Serial Number of the device that requests the URL
A URL could look like:
http://172.20.5.16/{mac}-{serial}/
let's assume {mac} = D8:DF:0D:00:11:22 and {serial} = 1-01-0000000001
In this case the webserver should provide the file:
http://172.20.5.16/D8DF0D001122-1-01-0000000001/
this enables the webserver to provide different config files to different devices, even though the same provisioning URL is set in each device.
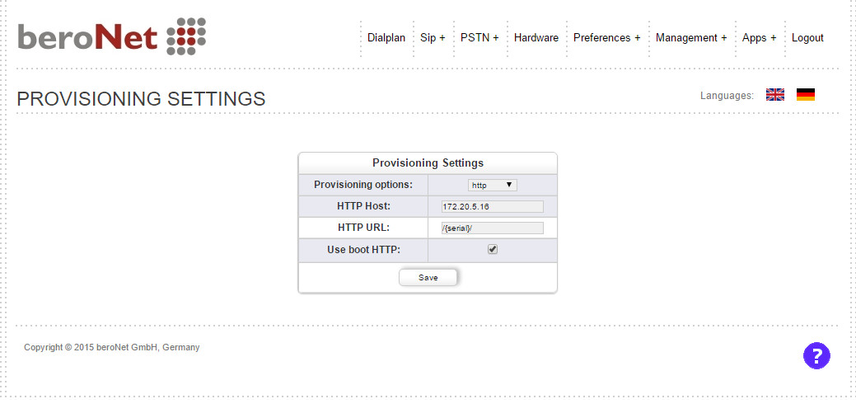
manual configuration via the GUI
This method is very simple, you can manually configure the provisioning URL under Preferences→Provisioning. You need to enable "Manual configuration" and then you need to define If the Provisioning should happen:
- provisioning method: tftp / http
- HTTP Host: only the servername or IP Address of the server
- HTTP URL: only the URL part where the config files reside
- Use boot HTTP: if the files should be provisioned on every boot
NOTE: in case of the tftp provisioning method, a TFTP Host and URL needs to be provided.
Please see the following example configuration:
After save & activate the device will attempt the provisioning after the next reboot.
configuration via the API
The beroNet API is described here: Using the beroNet Gateway & Card API. For Provisioning just a few API commands are required:
- ProvisioningSetConfiguration - sets the Provisioning URL, Mode and interval
- ProvisioningGetConfiguration - displays provisioning-configuration
- ProvisioningTriggerConfig - triggers immediate provisioning
- ProvisioningTriggerFirmware - triggers immediate provisioning of firmware
- ConfigurationActivate - activates configuration-changes
A sample API Call looks like:
http://172.20.5.10/app/api/api.php?apiCommand=ProvisioningSetConfiguration&Mode=once&Url=http://172.20.5.16/{serial}/
In this case 172.20.5.10 is the IP of the beroNet Gateway and 172.20.5.16 is the IP of the Provisioning Server.
The API will return:
ProvisioningSetConfiguration:success
if the request has worked. Or an error if e.g. a mandatory parameter is missing:
ProvisioningSetConfiguration:error:invalid_parameters
You can also check via the API if the ProvisioningSetConfiguration command has succeeded:
http://172.20.5.10/app/api/api.php?apiCommand=ProvisioningGetConfiguration
ProvisioningGetConfiguration:success:Mode:off;Url:http://172.20.5.16/{serial}/;
The following Command pipe can be used to provision the device via the API:
- set a provisioning URL for one time configuration updates
- trigger the configuration fetch mechanism
- activates the new configuration without reboot
http://172.20.5.10/app/api/api.php?apiCommand=ProvisioningSetConfiguration&Mode=once&Url=http://172.20.5.16/{serial}/
ProvisioningSetConfiguration:success
http://172.20.5.10/app/api/api.php?apiCommand=ProvisioningTriggerConfig
updateConfig:info:config_provisioning_enabled_by_server updateConfig:info:updated:hardware.conf updateConfig:info:updated:isgw.analog updateConfig:info:updated:isgw.cas updateConfig:info:updated:isgw.causes updateConfig:info:updated:isgw.conf updateConfig:info:updated:isgw.cpt updateConfig:info:updated:isgw.dialplan updateConfig:info:updated:isgw.gsm updateConfig:info:updated:isgw.isdn updateConfig:info:updated:isgw.sip updateConfig:info:updated:isgw.tdm updateConfig:info:updated:misc.conf updateConfig:info:updated:network.acl updateConfig:success:config_provisioning:beronet-D8DF0D0035F4-3-04-0000016254.config.xml ProvisioningTriggerConfig:success
http://172.20.5.10/app/api/api.php?apiCommand=ConfigurationActivate&Option=1
ConfigurationActivate:success
Automatic configuration via DHCP
The beroNet devices can be provisioned completely automatic via the DHCP server. This is called zerotouch provisioning and works in the following way:
- Default Network configuration is DHCP
- Device requests DHCP settings
- Device receive TFTP Option 66 AND 67
- Device starts provisioning of URL provided by option 67 on server provided by option 66
The URL has the same format as in the manual or API configuration, for example:
NOTE: Currently the Microsoft DHCP Server can not provision option 66, so DHCP provisioning will not work with the MS DHCP Server.
With udhcpd option tftp and bootfile needs to be set:
option tftp 172.20.5.16
option bootfile /{serial}/
# Static leases map
static_lease D8:DF:0D:00:19:4F 172.20.5.10
When the device boots it will use the URL to fetch its configuration. The device implicitly imports the configuration and activates it as well.
If you need scheduled remote assistance, you can request our on-demand support services: https://www.beronet.com/support